9 Things You need to know for Lead-Acid Battery
Since you’re reading this, you obviously have some questions about lead-acid batteries. For instance, how does a lead-acid battery work? For that matter, what exactly is a lead-acid battery?
Are these batteries still efficient enough for certain uses or are they obsolete? How do they compare to other batteries?
Fortunately, we have all the answers you’ve been looking for right here in this guide. To start with, we can assure you that these batteries are not obsolete. There are, in fact, many applications in which it’s ideal to use lead-acid batteries.
We’ll explain this in more detail below. We also provide a comprehensive explanation about what a lead-acid battery is and how it works. Read on to learn all there is to know about lead-acid batteries.
What Exactly Is the Lead-Acid Battery?
A lead-acid battery is a rechargeable battery that uses lead and sulphuric acid to function. The lead is submerged into the sulphuric acid to allow a controlled chemical reaction.
This chemical reaction is what causes the battery to produce electricity. Then, this reaction is reversed to recharge the battery.
Believe it or not, this technology is over 100 years old. However, it has been improved upon since its invention in 1859 and it now works more efficiently.

How Does the Lead-Acid Battery Work?
To put it simply, the battery’s electrical charge is generated when the sulphate in the sulphuric acid becomes bonded to the lead. The electrical charge is replenished by reversing this reaction. That is, the sulphate goes back into the sulphuric acid and, thus, the battery is recharged.
Now, obviously, there’s a finite amount of sulphate ions in the acid. And the available surface area of the lead it bonds to is limited, too. So, as the sulphate is depleted, the charge becomes weaker.
For this reason, lead-acid batteries are not ideal for powering devices for a long period of time. Instead, they’re best for applications that need a short, powerful burst of energy.
What Is the Amp Hour Rating?
12V Lead Acid Batteries are commonly used in a variety of applications. This ranges from automotive batteries to home energy storage solutions.
However, when selecting the right battery for any particular purpose, one of the most important considerations is the capacity rating.
This is also known as the amp-hour (AH) or milliampere-hour (mAh) rating and provides an idea of how much power this battery can deliver over a period of one hour without dropping below its minimum voltage level.
For example, a higher AH or mAh rating means that more energy can be drawn from the battery in a given period before it needs to be recharged.
Consumers should make sure they choose a battery with a high enough capacity to suit their needs.
The Self-Discharge of the Lead-Acid Battery
One unfortunate disadvantage of lead-acid batteries is that the chemical reaction described above can never be halted completely. In other words, these batteries will continue to discharge even when they’re not in use.
Normally, this self-discharge happens somewhat slowly, around 1% lost per day. But certain factors will increase this rate. For instance, the warmer the battery is, the faster it self-discharges.
Also, some devices use a little of the battery’s charge even when they’re turned off. The audio settings in your car are a good example of this. Your car radio uses battery power to “remember” these settings.
In any case, you’ll have to make sure you recharge your lead-acid batteries every once in a while or they will die.
Capacity of the Battery
A 12V Lead Acid battery has many uses, both in small and large applications. With this type of battery, it is critical to understand its capacity – which is measured in Amp-hours (Ah) or Milliamp-hours (mAh).
This is the amount of energy output from the battery before requiring a recharge.
This means that when you look at a 12V Lead Acid Battery, the higher the AH rating, the more power it will have. This will last for a longer time before it needs recharging.
Knowing and understanding your battery’s capacity is key to ensuring you get quality performance out of your purchase.
The Death of the Lead-Acid Battery
So, what causes a lead-acid battery to die? Certain factors can damage or change the materials that are needed to cause the necessary chemical reaction. One such factor is allowing the battery to remain in a partially discharged state for too long.
Partial Discharge
As the battery discharges, it lowers the amount of electrolyte solution (the sulphuric acid mixed with water). This leaves the lead plates partially exposed.
If they remain exposed, the sulphate that is already bonded to the lead can harden. Then, it remains on the lead permanently, which decreases the battery’s ability to recharge.
This partial discharge is a common problem with car batteries. You see, the battery recharges when you drive. But if you don’t drive often, or you always make very short trips, your battery might never get fully recharged.
Deep Discharge
Another common cause of battery death is deep discharge. This is when your lead-acid battery is discharged below 50%.
When this happens, small pieces of the lead plates can actually break off and sink into the electrolyte solution. Then, there is less material available to cause the chemical reaction. If too much is broken off, the reaction won’t happen at all.
This is why your car battery becomes unusable if you accidentally leave the headlights on overnight. Even if you’re able to jump-start the dead battery, the damage has already been done. The battery is permanently ruined and will have to be replaced.
Overcharging
Overcharging happens when you keep charging a battery that’s already full. Doing this can break down the material of the electrolyte. Once this happens, there is no sulphate left to bond with the lead.
This is why you don’t want to keep a lead-acid battery plugged into a charger all the time. It’s better to only plug it in once in a while.
Pros and Cons of the Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have powerful voltage for their size. Thus, they can power heavy-duty tools and equipment.
They can even power electric vehicles, like golf carts. However, in this case, you’d need to be careful to charge the battery often enough (and without overcharging it). If you don’t, the vehicle will die before reaching its destination, which will also damage the battery.
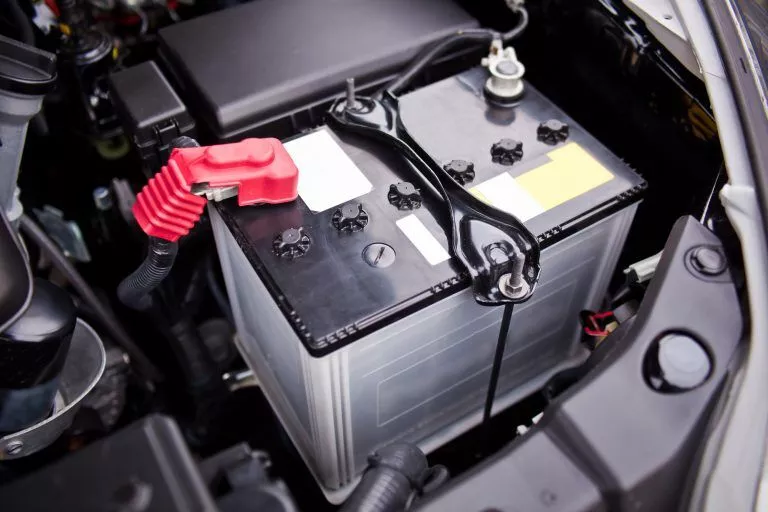
Additionally, lead-acid batteries are great for starting motor vehicles. They provide an intense jolt of energy to start the vehicle and then they recharge as the vehicle drives.
On the other hand, they are not good for devices you wish to use for long periods of time, like cell-phones. Also, they self-discharge when not in use, which will eventually kill the battery.
In other words, you can’t just leave them sitting around. Thus, they are a bad option for any application that will not be used frequently.
Regular Maintenance Is Essential
12V lead acid batteries are reliable power sources but require careful management to perform at their best. Charging and discharging should be closely monitored.
The batteries should never run out of power completely as this can make them not work as well.
Keep the batteries clean, and don’t forget to replace the electrolyte yearly. With these steps, you will ensure maximum capacity out of your 12V lead acid battery for years to come.

The Best Way to Maintain Lead-Acid Battery
One of the most important factors to consider when buying and using a 12V lead acid battery is its capacity. In general, these batteries have a much longer lifespan than other types.
But must still be regularly maintained in order to truly benefit from their longevity.
While charge levels should be monitored on a regular basis, and plates should also be cleaned with a cleaning agent suggested specifically for lead acid batteries.
One of the most important things a user can do to maintain their battery is to change the electrolyte annually on average.
Doing so will help ensure that your battery lasts as long as possible and continues to provide reliable power for years to come.
What Will You Use Lead-Acid Batteries For?
- Lighting systems for construction projects because of their long life cycle and ability to supply increased power for longer periods of use.
- Electric-powered vehicles, like golf carts, because they’re designed to sustain long-lasting energy, with a higher amp capacity and lower discharge rate.
- RVs and trailer homes.
- Backup power supply for UPS because the batteries can store more potential energy for future use in a longer time frame.
- Camping light sources that need a high energy capacity