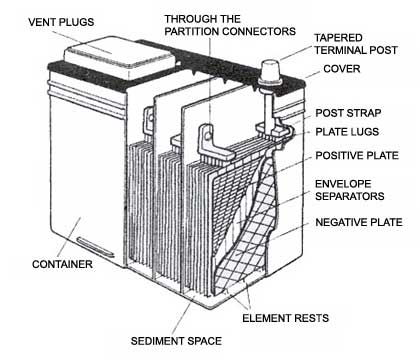
AGM BATTERY CONSTRUCTION
In AGM type batteries, the construction follows the same basics as standard SLA, with the addition of a fiberglass mat that is placed between each negative and positive plate to absorb the electrolyte. Since the mat acts like a sponge with the electrolyte, the battery becomes non-spillable.
The AGM battery holds the electrolyte in place and works by allowing the electrolyte to be passed through the fiberglass mat, creating maximum surface area for the electrolyte to touch the plates without it flooding the battery with too much fluid. AGM batteries contain only enough electrolyte to keep the mat wet and if the battery is broken no free liquid is available to leak out. This allows for less electrolyte in the battery while still providing the same energy as traditional SLA batteries.
How to Charge an AGM Battery
AGM batteries are ideal for a wide range of uses, from powering your electronic devices and cars to providing backup power to your UPS. If you don’t properly charge your AGM batteries the right way, however, they can prematurely age and die out much faster than they should. If you’re wondering how to charge an AGM deep cycle battery, read on to get to know some of the best charging practices to ensure your battery enjoys a long service life.
Charging AGM batteries properly is a very important step in ensuring a long service life. AGM batteries are used for a wide range of applications. For example, they are used in powering your electronic devices, providing backup power to your UPS, powering your car and storing renewable energy for future use. In order to ensure your AGM battery lives for years, it is critical that it is charged properly. If you charge your AGM batteries in the wrong way, they will face premature aging. Meaning, your batteries will die our much faster than they are designed to. In fact, improperly charging your AGM battery may cause the cells to preheat, damaging the battery and causing it to die within a matter of hours. In order to make the battery live for years, follow the 4 tips below for charging your AGM battery:
Invest in the right charger
Battery chargers are not designed to as a one-size fit all. Some chargers are designed to provide small amounts of power, while others are designed to provide a lot of power. Generally speaking, the larger the battery, the bigger the charger you’ll need. The opposite is also true. The smaller a battery is, the smaller charger you’ll need. When we’re talking about the “size” of the battery or the “size” of the charger, we’re not talking about the physical dimensions. In fact, we are talking about capacity, which is annotated in amperes (Ah).
Understand How Charges Affect Different Batteries
Many people believe that charging AGM batteries is similar to charging their laptop battery, but of course this is not true. In fact, the batteries used in laptops are a completely different technology. Laptop batteries are lithium while AGM batteries are lead acid. For this reason, charging AGM batteries is different and requires special charging procedures. For example, lithium batteries may be partially charged for a while without significantly harming the batteries. Charging AGM batteries requires you to fully recharge the battery. In fact, you’re supposed to slightly over-charge the batteries to give them a “top up”. Smart AGM chargers does that all for you, so you don’t need to worry if you’ve got one of those. If you repeatedly only partially recharge an AGM battery, let’s say up to 70% every time, the battery may actually lose it’s ability to fully recharge to 100% in the long term. This means the AGM battery would only be able to recharge up to 70%. To learn more about how charges affect different batteries.
Pay close attention to temperature
AGM batteries have a certain charge temperature range. This means if the temperature falls outside of this range, you should not be charging AGM batteries. For all types of lead acid batteries, you should avoid charging if the temperature raises above 40 degrees Celsius or 104 degrees Fahrenheit. Cold weather also affects charging AGM batteries. You should avoid charging your batteries if the temperature falls below 0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit. Ensuring the temperature is within the range of 0 and 40 degree Celsius is important while charging, in order to ensure the battery lives as long as it is designed to.
Expect the battery to warm up
Toward the end of charging AGM batteries, the cells may feel warm. This warmth is normal for lead acid batteries. In fact, you can still use the battery in your electronic devices while it’s warm. Please be careful and note that we are only referring to AGM batteries when claiming it’s fine to use them while they’re warm. This does not apply to small AA and AAA rechargeable batteries, which you may have picked up from your local grocery store. Furthermore, when referring to a warm AGM battery, we are not saying hot. If the battery is too hot, you definitely should not use it. However, if you place you hand on the battery and feel a bit of warmth, then it is normal. If you feel your AGM battery is getting too warm during the charging stage, you may give it a break by disconnecting the battery. Once the battery cools back down, then you can reconnect the charger to continue charging.
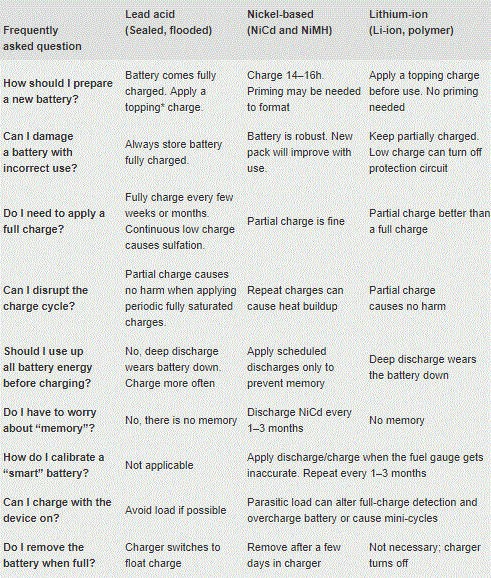
The table provides charging tips for three types of batteries:
- Lead Acid
- Nickel-based
- Lithium-ion
Please remember that the 4 tips mentioned above are for charging AGM batteries. The tips do not apply to Nickel-based or to Lithium-ion. However, this table was provided to you in order to note that there are many different types of batteries. It is also important to note that each battery type requires different charging specifications.
How fast can you charge an AGM Battery?
How long does it take to charge an AGM battery? First, the good news, of all lead acid batteries available (Flooded, Gel, AGM), AGM charges faster and more efficiently than the others. However, there are a few important factors to consider before determining the answer to this question. Once these questions are answered, then we can estimate the time it will take to charge an AGM battery.
Size Matters?
The old saying “size matters” is very true when it comes to charging batteries. In AGM the physical size of the battery will typically indicate the amount of energy the battery can store. The more energy stored; the more energy that will need to be put back into the battery after it’s been used.
The Red Cup
The next factor we must account for is the power output capability of the charger. Imagine it in terms of filling up a swimming pool with water and using a Solo Red Cup. But what if we were talking about a kiddie pool, nay a Barbie pool? Then the Red Cup might even be too big and harm the battery. Because we are returning energy to the battery, a 12V, 2A (24W) charge tender is going to take a lot longer to recharge a battery than a 12V, 25A (300W) charger, while at the same time using this 300W charger on the 420W is like filling the Barbie pool with a garden hose. Charging is all relative like our Red Cup analogy notes.
Goldilocks
And there’s one other thing to consider when choosing a charger, the Goldilocks principal. We don’t want to go too small (undercharge) or too big (overcharge), but we want it to be “just right”. Fullriver batteries can be charged with more amperage than a typical flooded or gel battery. We advise at a minimum 10% of rated capacity but recommend 25% in amp output from the charger (e.g., 100Ah battery should be charged with a minimum of 10A, but we recommend using a 25A charger to achieve 25%).
Are we there yet?
Finally, we can begin to answer the question that we started with using simple math. To determine how long it will take to charge an AGM battery, simply divide the rated capacity of the battery at the 20hr. rate by the amp output of the charger, and then multiply by 1.33 to account for the balancing phase of the charging and the natural aging of the battery.
Ah/A*1.33= ~Charge Time (H)
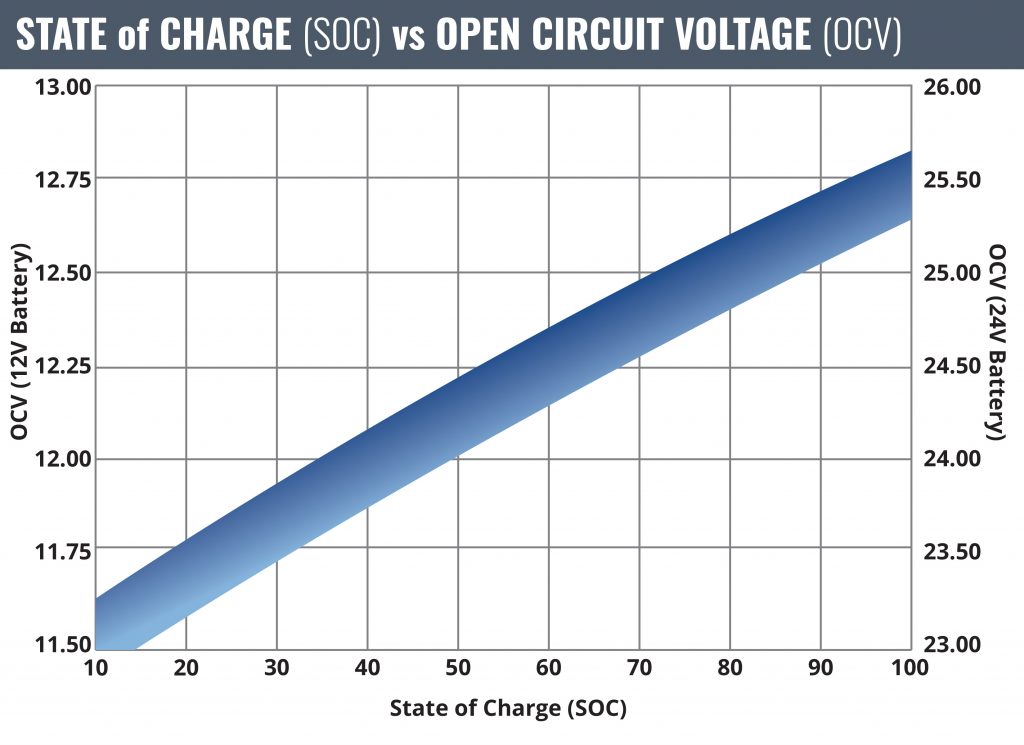
100/25*1.33= ~5.58 or ~5hrs 30mins Of course, this accounts for a fully discharged battery, and gives a very good picture of how long recharging typically will take. In the real world you can perform this same exercise and get pretty close to the actual time by referencing the open circuit voltage (OCV) of the battery to our chart below:
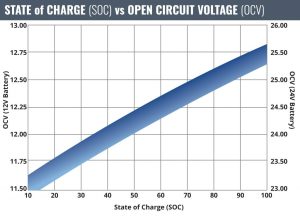
In summary, we have seen that pairing the right sized charger and battery can make a great difference in charging a battery as quickly and efficiently as possible. Determining how much time recharging will take is just some simple math and a bit of estimation.
Did you already know this about recharging batteries? We’d love to hear some of your experiences with recharging batteries!
How to Increase Your AGM Battery Lifespan
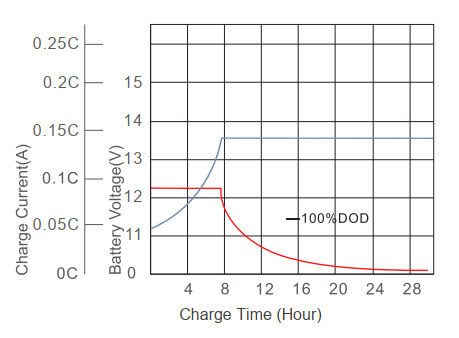
Three Stages Charging
The THREE STAGES CHARGING are Constant Current charge (bulk charging), Constant Voltage charge (absorption charge), and Supplemental charge (float charging).
The 1st stage is constant current charging, CC for short name. We set the charger voltage to the battery (pack) cycle charge voltage, and the current to the cycle charge current. Please note that too high voltage or too high current will overcharge the battery and damage the battery. The specific voltage and current will be explained in detail in the next 2 parts. During this phase, the battery voltage rises to a constant number.
The 2nd stage is Constant Voltage, where the battery voltage remains at a constant value and the charge current decreases. After the current is reduced to a very small value, stage 3 begins, reducing the voltage to the float voltage.
The 3rd stage is supplemental or trickles charge. The battery current is shallow, and this phase is critical to activate the whole materials inside the battery, which helps to maintain a good health condition of and extend the lifetime.
Charge Voltage
The charge voltage includes cycle charge voltage and float charge voltage, fast charge voltage. In general, the float charge voltage is used for daily floating charges, the lowest. Cycle charge voltage is used for recharging after discharged to a certain depth, it is higher. Fast charge is the voltage of rapid full charge under an emergency condition, the highest, not commonly used.
The nominal voltage of a single AGM battery cell is 2V. In different combinations, the popular voltages are 2V, 6V, 12V. 24V and 48V are also found in battery banks. Specific cycle charge voltage and float voltage refer to the following table. All parameters are generally based on 25°C. Please note that the appropriate voltage is different for flooded or gel batteries.
| Battery(Bank) Voltage | Cycle Charge Voltage | Float Charge Voltage |
| 2V | 2.40V~2.50V | 2.25V~2.30V |
| 6V | 7.20V~7.50V | 6.75V~6.90V |
| 12V | 14.4V~15.0V | 13.5V~13.8V |
| 24V | 28.8V~30.0V | 27.0V~27.6V |
| 48V | 57.6V~60.0V | 54.0V~55.2V |
On regular basis at 25°C for 12V deep cycle AGM batteries, float charge voltage is 13.5V~13.8V, cycle charging voltage is 14.4V~15.0V.
Some batteries are marked with charge voltages on the label or print, including float charge voltage and cycle charge voltage. For example, as shown in the above photo, the float voltage is 13.5V~13.8V, and the cycle charge voltage is 14.4V~14.9V. You can use the charge voltage directly. Or you can also choose the safer intermediate value or minimum value. The highest value of the cycle charge voltage (15.0V) could be considered as the fast charge voltage, which is always considered to cause damage to the battery.
Charge Current
The charge current is related to the rated capacity of the battery. It is generally 0.1C~0.4C, which is 1/10 to 4/10 of the rated capacity.
If it is a 100Ah battery, it is 10A~40A. It can be measured with a DC ammeter, a clamp meter.
Well, some of the most advanced manufacturers on the market today use thin plate technology. They increased the charging current to 1C, which is equal to the rated capacity. High-current charging will greatly shorten the charging time, but these high-end batteries are not popular enough.
Still, 0.1C~0.4CA are considered in most of the applications.
Charge Temperature
The charge temperature of AGM battery is between 0℃ and 40℃, please keep the charging temperature within this range, otherwise, it is harmful to the battery.
Charge Connection
There is not much to say, the positive pole of the charger is connected to the positive pole of the battery, the negative pole of the charger is connected to the negative pole of the battery, then the charger and the mains are turned on, then the battery is charging.
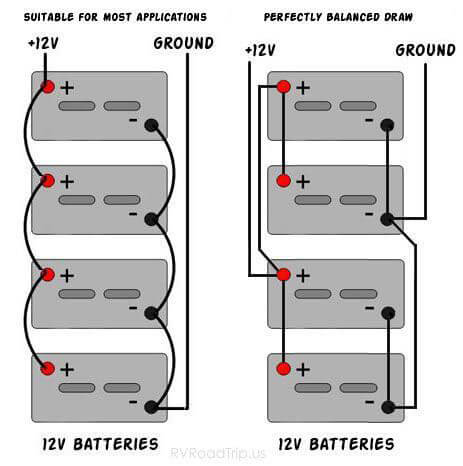
It is worth mentioning that for multi-cell battery charging, I recommend parallel charging. Because parallel charging can improve the consistency of the battery, and low-voltage charging is also safer.
It should be noted that when charging in parallel, the cable should adopt the diagonal method to improve the consistency of the current shunt. The so-called diagonal connection method is as follows.
Tag in this article: #AGM Battery
Tips: more detail information, for acid battery。