17 Tips to extend the life of your car battery
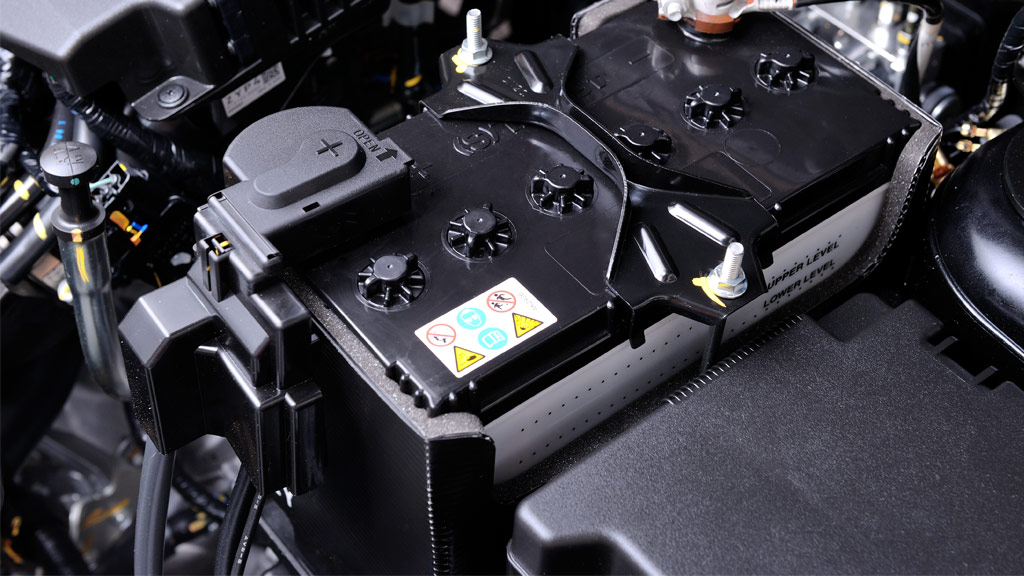
When it comes to cars there’s nothing worse than being stuck with a flat battery. We’ve all been there at some point in our lives, and the problem is often made worse from the fact that with modern vehicles there is little to no warning signs shown prior – and probably a 50% chance that it’ll occur while you’re out and about away from home.
Just like the battery in your mobile phone or laptop, lead-acid car battery has a limited life span and will eventually lose their ability to hold sufficient charge to start your car. On average you can expect a lead-acid battery to last around 42 months, but this time-frame will vary depending on a number of variables – such as hot or cold climates, journey lengths and the performance of your car’s charging circuit.
But regardless of what conditions your car is subjected to, here are 17 tips you can consider to help get the very best out of your battery.
1. Avoid driving short trips often
Your battery is given a workout every time you start your car, but is then recharged by the engine during the journey. So if you are only driving a short distance it will be impossible for the battery to regain the amount of power lost – and if you repeat the process daily the battery voltage will reduce steadily until it can no longer start the car.
Maintain your car’s battery power by driving it frequently and for longer periods of time – and if you don’t use your car very often, consider investing in a battery charger to help maintain the correct voltage.

2. Keep your car battery tightly fastened
Vibration can reduce the life of your car battery, so it is vital that you always use an approved battery clamp to ensure it is properly held down at all times. If not securely fastened, excessive vibration could damage your battery’s internal components – creating short circuits and reducing car battery life.
But don’t make the mistake of over-tightening the battery clamp nuts to the limit of your strength – because you might damage the car battery! Instead, simply tighten the nuts until you feel the resistance start, and then continue for only an additional half turn.
3. Minimise power used while engine is off
Car batteries are happiest when they are kept close to 100% charge – so keeping your headlights or interior lights on while the engine isn’t running is a big no-no. Before exiting the vehicle, always ensure that all accessories are turned off and double check that the lights are off as you walk away.
4. Keep your car battery clean
Ensure the top of your car battery is clean, dry, and free of dirt and grime. A dirty battery can discharge across the grime on top of the casing – creating a mild short circuit which will eventually flatten the battery.
The battery terminals will also corrode over time, and keeping them clean from buildup is a great way to extend the life of your car battery. Scrub the terminals with an old toothbrush dipped in a baking soda and water mixture. Then, using a spray bottle with cold water, rinse the mixture off and follow up with a thorough drying with a clean cloth.
5. Try to minimise heat exposure
A popular misconception is that cold weather kills car batteries – but this is not strictly true. Car batteries do have to work harder to start your engine during the winter months, but the reason why so many fail during winter is mostly due to damage they sustained during the heat of the previous summer.
Extreme heat is hard on batteries because it increases the rate of water evaporation from the cells – even in sealed top batteries. The cold then reveals the shortcomings of the weaker battery, as lower temperatures sap the remaining cranking power as it tries to start cold engines with thick oil.
So what can you do? Well, basically anything you can think of to reduce the temperature subjected to the battery. Parking your vehicle in the shade where possible and keeping your vehicle garaged while not in use are both great ideas – or you can look at ways to help insulate the battery from heat generated within the engine bay.
6. Check your car battery’s voltage once a month
A lead-acid battery’s life will shorten dramatically the longer it is left partially or fully discharged, so checking the voltage with a voltmeter once a month is a great way to keep an eye on your battery’s health. A healthy, fully charged lead-acid battery should have a voltage of around 12.7 volts or above.
Should the voltage drop below 12.5 volts, we’d recommend recharging the battery as soon as possible. It is also important to remember that a lead-acid car battery is considered to be half charged at 12.4 volts, and completely flat / dead at 12.0 volts – so don’t get complacent.
7. Don’t leave the car unused for long periods
As you might have noticed in some of the points above, it is vital that lead-acid car batteries are kept fully charged at all times to prevent damage. Regardless of the brand, all lead-acid batteries will naturally lose charge over time – something which is referred to as ‘self-discharge’.
A flooded lead-acid battery will self discharge at a rate of around 1% per day at room temperature, 0.25% per day at 10°C (50°F) and 1.5% per day at 30°C (86°F). It is important to remember that parasitic loads from the vehicle will increase the rate of discharge, so if your vehicle is going to be sitting unused for any longer than a week it would be advisable to connect a trickle charger to keep the battery in tip-top condition.
8. Depth of Discharge
A battery’s depth of discharge (DoD) refers to how deeply it has been discharged. To ensure that your battery lasts as long as possible, make sure you don’t over-discharge it. If you fully discharge a battery only once, you can cause irreversible damage, and if you discharge it 100% frequently, you will shorten its lifespan. Thus, a 3 or 4-year car battery may only last you one or two years.
A car battery’s cycle life is the number of charges and discharges that it can complete before its performance starts to decline. A battery’s cycle life is affected by how deeply it is discharged. Although Tall Tubular and AGM deep cycle batteries are designed for deep discharge, they are not meant to be fully discharged.
If you only discharge your Tall Tubular and AGM deep cycle batteries to 50% before recharging them, you will significantly extend their lifespan. However, in countries like Nigeria, where the grid’s power is neither predictable nor reliable. Many people discharge their inverter batteries up to 80% out of necessity.
While regularly discharging a Tall Tubular or AGM deep cycle battery beyond 80% will significantly shorten its life. A lithium battery, on the other hand, can be depleted to 90% of its total capacity (10% SOC) without any repercussions.
The cost of a lithium battery is high, however, making AGM and Tall Tubular the options that give the highest return on investment. Regardless of the type of battery, you are using. When you hear your power inverter’s low battery alarm, turn it off. Do not allow your power inverter to shut off on its own.
When an AGM battery (at an average temperature of 25 °C) reaches 80% depth of discharge, the battery provides approximately 400 cycles or just over 1.5 years (if cycled daily), and with 30% depth of discharge, the battery offers 1200 cycles.
9. Perform Regular Battery Cycles
Your 12v inverter battery goes through cycles when you use it. You have completed a cycle when you have used 100 per cent of the battery’s capacity. Recharging your battery after discharging it to 50% is not considered a full cycle. Repeating the same action, however, counts as one cycle
Battery cycles can have a major impact on battery life. It is harmful to the battery’s longevity to keep it fully charged for extended periods without using it.
A fully depleted battery can also reduce its ability to hold a charge if you leave it sitting for a long time without charging. Performing regular battery cycles will extend the life of your battery.
10. Use a High Quality car Battery Charger
Incorrect charging is a major cause of battery failure. In the market, there are many batteries with different chemistry, as well as guidelines on how they should be handled and charged.
It can be fatal to use a charger not designed for your battery size and chemistry. Inverter battery chargers should charge batteries as reliably and effectively as possible. Whenever possible, use an inverter or charger from the same manufacturer as the batteries
While some chargers damage batteries as they charge them, others heal and repair them as they charge. There is a significant difference between a high-quality battery charger and a low-cost battery charger that, if used incorrectly, might destroy your battery.
The high-quality chargers are often three-stage and offer a variety of safety measures, such as not allowing electricity to flow until the battery is properly attached. They may also be fan-cooled and have features such as automated temperature adjustment, short circuit protection, and other similar functions.
The low-cost battery charger lacks the above-mentioned safety measures and does not automatically reduce the voltage after the bulk charge has been completed.
If this type of charger is left unattended, it is possible to do substantial harm to your battery, possibly to the point of severe failure. Before charging your deep cycle batteries, make sure you’ve read the instructions and have taken all necessary measures. By measuring the voltage on a regular basis, you may obtain a decent indication of your batteries’ state of charge
11. Use a Battery Equalizer
When two or more batteries are connected in series, installing a battery equalizer system is an inexpensive way to extend the life of your batteries. Battery equalizers are easy to install and maintain, so they are an excellent investment for batteries.
In order to equalize the voltage of the battery system, a battery equalizer system transfers energy between connected batteries. The system can compensate for both batteries when there is a voltage difference of more than 10 mV
AGM, Tubular and Lithium batteries can all benefit from battery equalizers because they can maintain a state of equilibrium for extended periods of time.
You should not use a battery equalizer with deep-cycle GEL batteries. Equilibrating GEL batteries will cause permanent damage.
12. Temperature
Temperature greatly affects the life of a car battery. Temperature swings affect all batteries, no matter what type they are, tall tubular, AGM, GEL or lithium battery. Generally, deep cycle batteries should be charged and maintained between 50-95 degrees Fahrenheit, or 10-35 degrees Celsius.
In order to maintain its life, a battery should not be exposed to extreme temperatures – hot or cold -. Battery life and efficiency are significantly reduced by extreme temperatures, which stress the battery.
13. Correctly Size Battery Bank
According to Peukert’s law, when using lead-acid deep cycle batteries the faster the rate of discharge, the lower the capacity of the battery. A battery bank should be correctly sized for the load it is intended to carry. Using the incorrect size battery bank will result in performance problems.
Sulphation can result from draining your battery too quickly. Lead sulphate crystallizes on the cathode of a lead-acid battery, diminishing the conductive surface area and limiting the amount of current available, thereby depriving the battery of maximum power. Deposition of lead sulphate crystals is the main cause of lead-acid battery degradation and early death
14. Use energy-saving devices
Utilize energy-saving technologies to reduce the power you draw from your inverter batteries. A conventional bulb uses 75 per cent more energy than a CFL or LED. A ceiling fan with superior copper wire uses less energy than one with poor copper winding (poor copper winding increases resistance and increases the load on inverters).
15. Keep car battery clean and corrosion free.
Make sure your car battery terminals are free of corrosion and rust which lowers the performance of your battery and reduces the current flow. As a result, battery life is lessened and backup times are shorter.
A solution of hot water and baking soda can be poured on the terminals of your battery to prevent rusting, and vaseline or petroleum jelly applied to prevent further corrosion.
16. Do not mix car battery of different age, type or size
For optimal performance and lifespan. Do not mix batteries of different ages, types or sizes. For example you should not mix flooded and sealed lead acid batteries because the charge profiles of both of these are slightly different.
Each car battery contributes to the total voltage when batteries are connected in series. This voltage drops when one eventually fails, perhaps because of sulfation. You should change the entire battery bank, with new batteries. Individual batteries shouldn’t be replaced, since they would be out of balance with the older ones.
A new car battery has a low resistance, which increases as it ages. Joule’s law states that thermal energy gain accompanies loss of electrical energy. In this way, when old and new batteries are mixed, too much energy passes through an abnormally high resistance. The new batteries run out sooner, while the old batteries overheat. We waste good money when we mix old and new.
17. Top Up car Battery With Distilled Water
Wet cell batteries need to be topped up regularly with Distilled water. You should never fill a car battery with normal water. It will damage it and if you don’t top up at the appropriate time and with the proper amount, your battery’s performance and lifespan will suffer.
Distilled water should always be added after the battery has been completely charged. There should be enough water to cover the plates before charging. The water level should be above the plates if the battery has been depleted (partially or totally).
After a complete charge, keep the water level at the proper level to avoid having to worry about the water level in a different state of charge. We recommend checking batteries once a month until you get a sense of how often they need to be topped up.
Safety Precautions:
Always use insulated tools when working on batteries.
Remove all rings, watches, bracelets, and other metal jewellery.
Wear protective clothing at all times.
Safeguard your eyes by wearing protective eyewear.
When handling batteries, do not smoke or expose a naked flame.
Make sure the places where batteries are stored or charged are adequately ventilated.
If acid is spilled on skin or clothing, wash with plenty of clean water
If acid comes into contact with eyes – wash with plenty of clean water and seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusions
This guide gives you 17 simple ways to extend the life of your inverter car battery. It is important to keep in mind when buying a inverter car battery for home or office, that a quality battery brand together with a warranty should be your main concerns, and not inverter battery prices.
That being said even the best car battery in the world won’t last very long. If you don’t take good care of it. Ultimately, the key to extending the life of your deep cycle inverter battery is to start with the best car battery combination and continually perform basic maintenance. The components listed above are clear and concise methods of prolonging the life of your battery, saving you time, money, and frustration in the long run.
Stop-Start Battery Related Products:
Related Products Application: