12V LiFePO4 Battery Pack Characteristic Curve
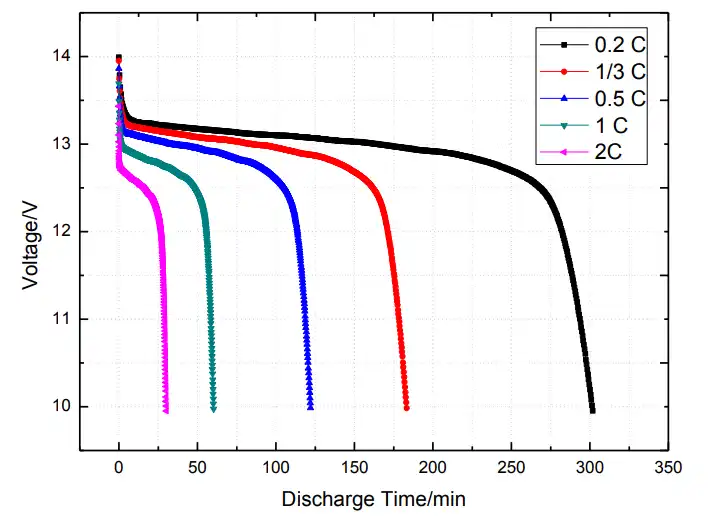
1. Discharge Curve at Different Discharge Rate
Different Rate Discharge Curve @ 25 0C
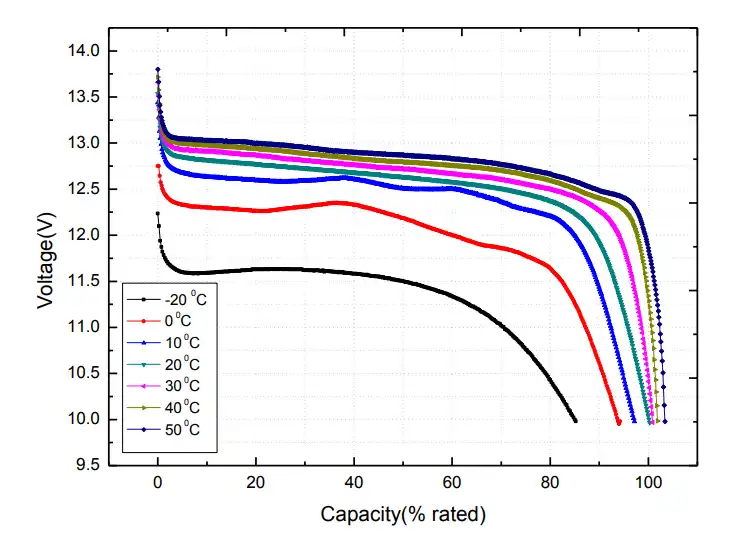
2. Different Curve at Different Temperature
Different Temperature Discharge Curve @ 1C
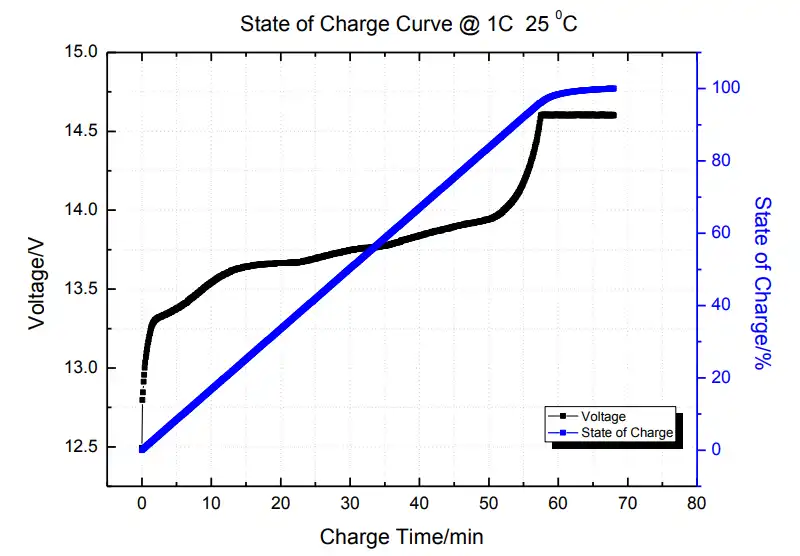
3. State of Charge Curve
State of Charge Curve @ 1C 25 0C
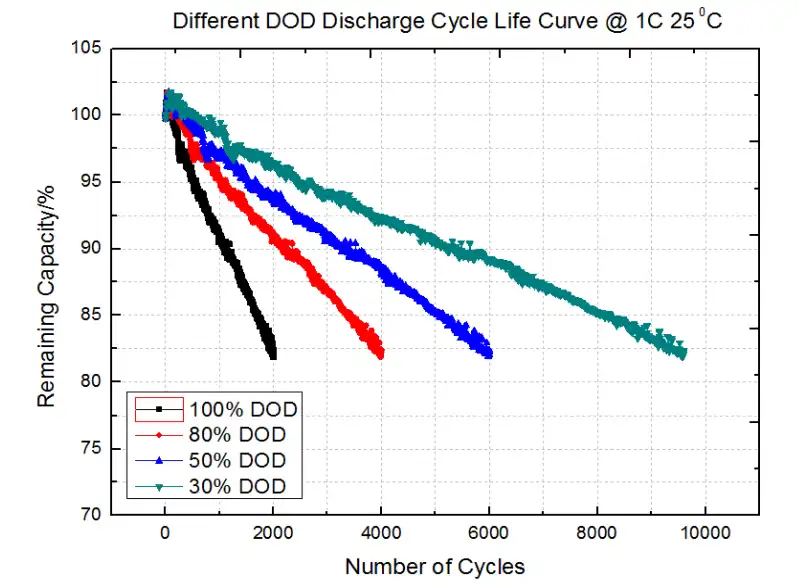
4. Cycle Life Curve at Different DOD
Different DOD Discharge Cycle Life Curve @ 1C 25 0C
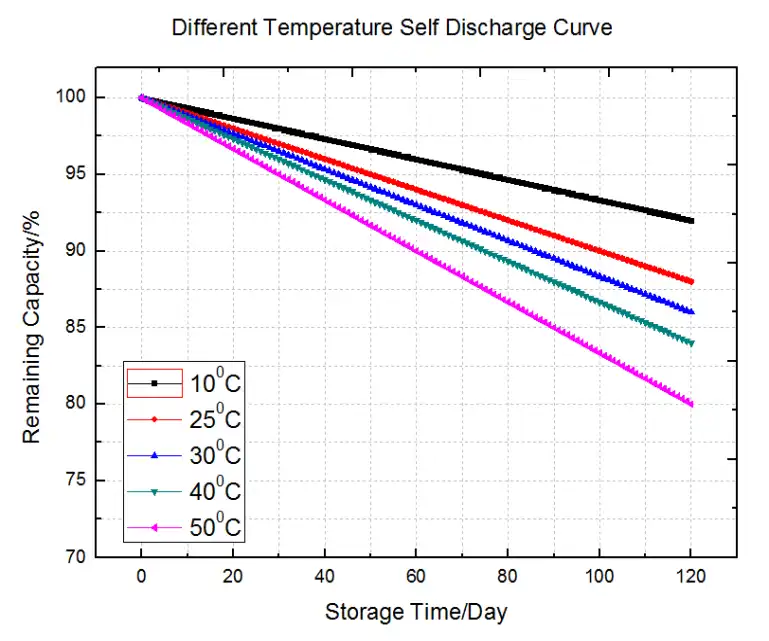
5. Self Discharge at Different Temperature
Different Temperature Self Discharge Curve
Here are LiFePO4 battery voltage charts showing state of charge based on voltage for 12V, 24V and 48V batteries — as well as 3.2V LiFePO4 cells.
Note: These charts are all for a single battery at 0A. Consult the manual of your LFP battery for its specific discharge curve and voltage parameters.
12V LiFePO4 Battery Voltage Chart
| Voltage | Capacity |
|---|---|
| 14.6V | 100% (charging) |
| 13.6V | 100% (resting) |
| 13.4V | 99% |
| 13.3V | 90% |
| 13.2V | 70% |
| 13.1V | 40% |
| 13.0V | 30% |
| 12.9V | 20% |
| 12.8V | 17% |
| 12.5V | 14% |
| 12.0V | 9% |
| 10.0V | 0% |
12V 100Ah LiFePO4 batteries are currently some of the most popular for off-grid solar power systems. They’re a drop-in replacement for 12V lead acid batteries, and a great upgrade.
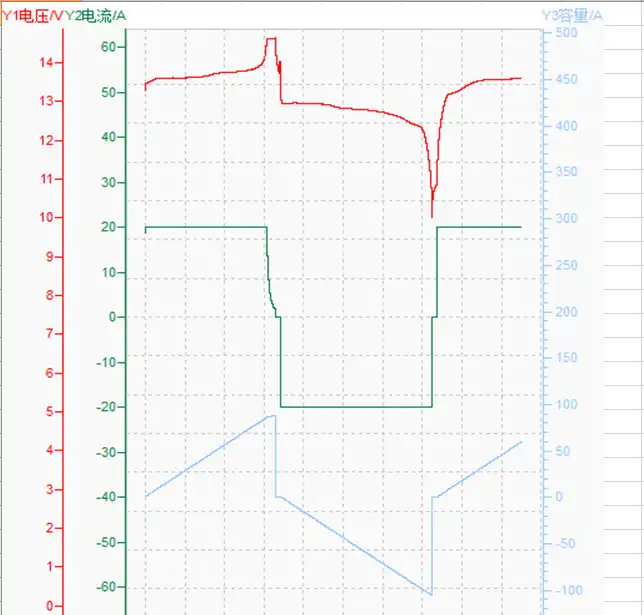
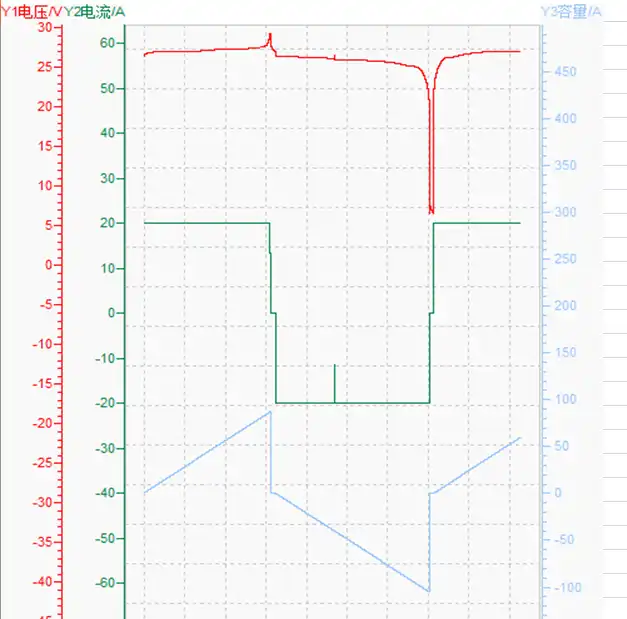
12v100ah-discharging-and-charging-curve-02
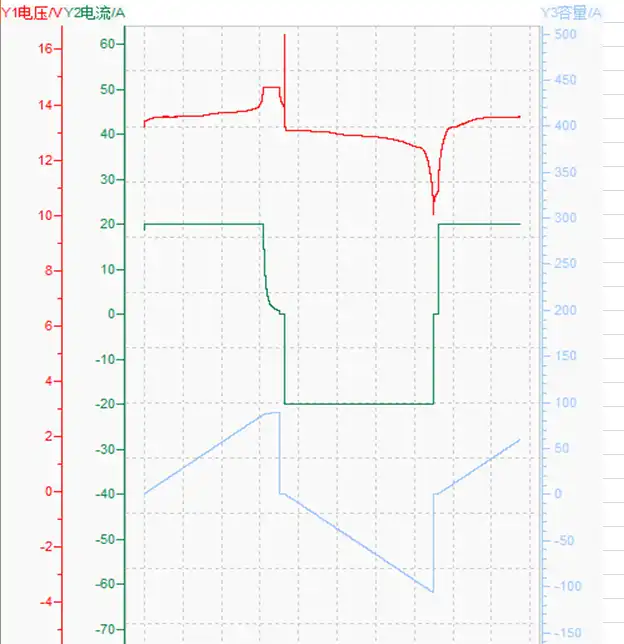
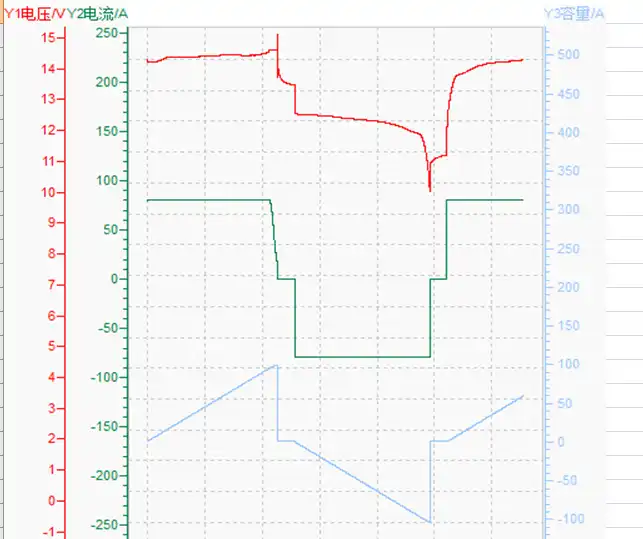
24V LiFePO4 Battery Voltage Chart
| Voltage | Capacity |
|---|---|
| 29.2V | 100% (charging) |
| 27.2V | 100% (resting) |
| 26.8V | 99% |
| 26.6V | 90% |
| 26.4V | 70% |
| 26.2V | 40% |
| 26.0V | 30% |
| 25.8V | 20% |
| 25.6V | 17% |
| 25.0V | 14% |
| 24.0V | 9% |
| 20.0V | 0% |
24V lithium iron phosphate batteries are another popular option for solar power projects. You can either buy an off-the-shelf 24V battery or pick up two 12V batteries and connect them in series to make a 24V battery bank.
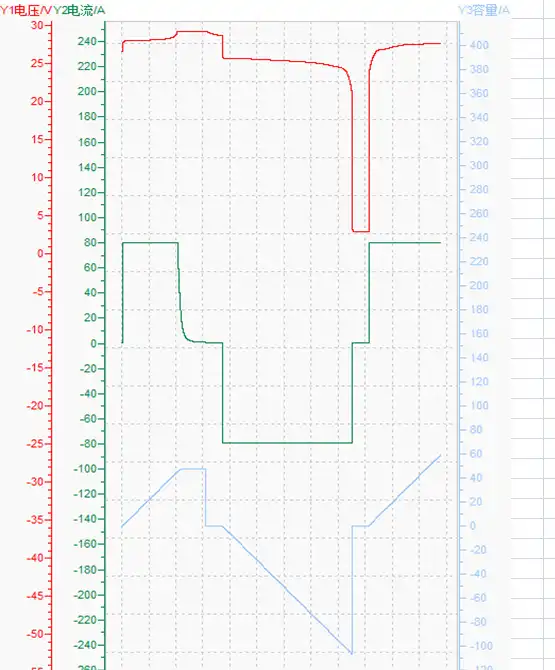
3.2V LiFePO4 Cell Voltage Chart
| Voltage | Capacity |
|---|---|
| 3.65V | 100% (charging) |
| 3.4V | 100% (resting) |
| 3.35V | 99% |
| 3.33V | 90% |
| 3.3V | 70% |
| 3.28V | 40% |
| 3.25V | 30% |
| 3.23V | 20% |
| 3.2V | 17% |
| 3.13V | 14% |
| 3.0V | 9% |
| 2.5V | 0% |
3 Ways to Check LiFePO4 Battery Capacity
1. Measure Battery Voltage with a Multimeter
Pros: Moderately accurate
Cons: Must disconnect all loads and chargers and let battery rest
Battery voltage changes depending on charge and discharge rates. Plus, LiFePO4 batteries have a relatively flat discharge curve from around 99% to 20% capacity. Because of these factors, it can be hard to estimate their state of charge from voltage alone.
To get an accurate estimate of battery capacity based on voltage, you first need to disconnect any loads and chargers from the battery. (Don’t forget to disconnect your solar panels from your charge controller first!)
Let the battery rest for a little while — I usually wait 15 minutes — and then measure its voltage with a multimeter.
Compare your measurement to the right voltage curve above, or the state of charge chart in your battery manual. Use it to get a rough estimate of your battery’s remaining capacity.
For example, I own the BravaBattery 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 Deep Cycle Battery. I wanted to check its capacity after having stored it for 3 weeks. I brought it out of storage and measured its voltage with a multimeter. I got 13.23 volts.
I then compared this number to the 12V LiFePO4 state of charge chart above, as well as the one in the battery manual. Based on the charts, I’d estimate my battery’s state of charge was somewhere around 80%.
I like this method best for estimating the state of charge of an LFP battery I’ve just received or just pulled out of storage. The battery is already at rest and not connected to anything. I find it too inconvenient to disconnect everything once the battery is in use.
DIY lithium battery builders will also measure the voltage of used (and new) battery cells — such as LFP cells and 18650 lithium batteries — to see which are good and which are duds.
2. Use a Battery Monitor
Pros: Most accurate, convenient
Cons: Good battery monitors are expensive
The best way to track battery capacity is to connect a good battery monitor — such as the Victron SmartShunt or Victron BMV-712.
Battery monitors track the amount of amp hours consumed to accurately estimate the state of charge. They also display useful system specs such as battery voltage and current. Some connect via Bluetooth to your phone so you can check your LiFePO4 battery’s capacity in a mobile app.
3. Use a Solar Charge Controller
Pros: Convenient
Cons: Inaccurate
You may be thinking:
“My solar charge controller already measures battery voltage. I can just use it to check battery capacity.”
But!
This voltage reading is inaccurate. It suffers from all of the problems mentioned above, plus it’s done while the battery is connected to loads and chargers.
(Not to mention that some charge controllers just have flat out wrong voltage readings.)
For example, recall that when I checked my battery’s voltage with a multimeter at the battery terminals, I got a voltage reading of 13.23 volts. That correlates to a roughly 80% state of charge.
But when I connected my battery to an MPPT charge controller, the controller measured 13.0 volts. That correlates to a roughly 30% state of charge — a difference of 50%! Granted, some charge controllers have much more accurate battery voltage readings than others.
After all, voltage drops under load. And a charge controller is a load. If I were to connect a solar panel and start solar charging the battery, its voltage would instantly jump.
Checking battery capacity this way is convenient. But beware that it can be quite inaccurate. I generally use this voltage reading just to make sure my battery isn’t close to being fully discharged.
If you use this method and want to make sure it’s as accurate as possible, you can buy a battery voltage sensor, such as the Renogy Battery Voltage Sensor or Victron Smart Battery Sense. A voltage sensor gives the controller a more accurate voltage reading, especially in solar power systems with long wire runs.
LiFePO4 Voltage FAQ
What is the voltage of a fully charged 12V LiFePO4 battery?
A fully charged 12V LiFePO4 battery will have a charging voltage of around 14.6 volts and a resting voltage of around 13.6 volts.
How much can you discharge a LiFePO4 battery?
Many LiFePO4 batteries can discharge 100% of their rated capacity every time with no ill effects.
However, many manufacturers recommend discharging only 80% to maximize battery life. In fact, some brands state the cycle life of their batteries based on 80% depth of discharge (DoD).
For comparison, lead acid batteries can only discharge 50% of their rated capacity. So a 12V 100Ah LFP battery has as much usable capacity as a 12V 200Ah lead acid battery.
What is the low-voltage cutoff of a 12V LiFePO4 battery?
The low-voltage cutoff of many 12V LiFePO4 batteries is around 10 volts. The BMS should detect when the battery voltage falls below 10 volts and enter a sleep mode to protect the battery cells from over discharge.
Low-voltage cutoff is also called low-voltage disconnect, which you’ll sometimes see abbreviated LVD.
Note: Some batteries have higher cutoffs, such as 10.6V. So the limit in your battery manual may not be exactly 10V.
LFP batteries in sleep mode can have very low voltage readings, usually less than 5 volts. You may think that the battery is dead, but really it’s just sleeping.
Once a battery enters sleep mode, it needs to be woken up. Refer to your battery manual for how to do this. It usually involves jump starting it with another 12V battery.
What is the float voltage of a 12V LiFePO4 battery?
LiFePO4 batteries don’t need to be float charged because they don’t leak charge the way lead acid batteries do.
If you can, disable float charging on your charge controller or battery charger. If you can’t, prevent the battery from entering float charge by setting the float voltage to that recommended in the battery manual — usually 13.6 volts ± 0.2 volts.
For long and happy LFP battery life, in order of importance, you should be mindful of the following:
- Keep the battery temperature under 45 Centigrade (under 30C if possible) – This is by far the most important!!
- Keep charge and discharge currents under 0.5C (0.2C preferred)
- Keep battery temperature above 0 Centigrade when discharging if possible – This, and everything below, is nowhere near as important as the first two
- Do not cycle below 10% – 15% SOC unless you really need to
- Do not float the battery at 100% SOC if possible
- Do not charge to 100% SOC if you do not need it
LifePO4 Batteries Related Products:
Related Products Application:
LifePO4 Batteries Related Posts:
Tag in this article: #LiFePO4 Battery
Tips: more detail information, for deep cycle LiFePO4 battery。